imputed cost in Hindi imputed cost meaning in Hindi
Contents
Normal profit is an additional amount over the monetary and imputed cost that must be received by an entrepreneur to induce him to produce the given product. Normal profit is the entrepreneur’s opportunity cost and therefore enters into the cost of production. Opportunity cost is the value of the opportunity or alternative that is sacrificed. We may be wondering how it is that profit is an element of cost. We will try to understand it. Implicit cost is simply an opportunity cost that a company incurs when it uses resources to make a decision.
- Basically, the concept of imputed value is logical for a time set or an item, wherein the real value has to be ascertained.
- It’s easy to calculate if you’ve narrated the notes of your business costs.
- Electricity, water, and internet service are examples of utilities that are required to keep a business running.
- This cost is not reported separately but is not included in the accounting profit.
- If you spend 5 hours playing video games, for example, you will not be able to study during that time.
An avoidable cost is an expense that will not be incurred if a particular activity is not performed. Many times, we find that all inputs are not always bought or hired by the producer from the market. Some of the inputs are provided by the entrepreneur or producer himself. He may invest his own money in the business.
(a) Paid out cost is ____________ (explicit cost, implicit cost).
This choice will have an opportunity cost linked with it. With this value, best guess estimation can be executed to precisely evaluate a large set of data points or a series of values. 2.The imputed costs of crimes averted as a result of a gang injunction can greatly outweigh the cost of the injunction’s enforcement.
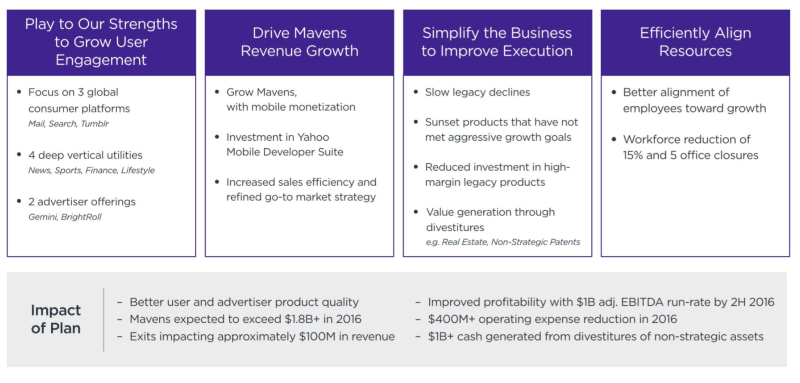
He may be the manager of his own firm. A farmer may cultivate his own land. If a producer had taken a building from another production unit, he would have paid rent. In the same way, if he had borrowed money he would have paid a certain amount of interest. Similarly, if he had engaged a manager he would have paid him a salary.
(h) Wages paid
Implicit cost is the cost incurred when an entity uses the owner’s resources such as capital inventory and so on. Both implicit and explicit costs are included in the opportunity cost. An explicit cost is a cost that requires a payment. Implicit costs are costs that don’t require a payment. Calculating explicit costs is simple as long as you know your business expenses.
To find total cost we have to ____________total variable cost . The term explicit refers to something that is stated explicitly or in great detail. This is the only accounting cost that is required to calculate profit, and it has a direct impact on a company’s bottom line. Implicit cost refers to an individual or company’s cost but has not been reported separately. An example of an implicit cost is when a business owner who owns a start-up doesn’t take a salary during the first days.

It accepts no liability for any damages or losses, however caused, in connection with the use of, or on the reliance of its product or related services. Terms and conditions of the website are applicable. Also called as estimated imputation, imputed value is regarded as an assumed value that is provided to an item when the real value is unknown or unavailable. Basically, the concept of imputed value is logical for a time set or an item, wherein the real value has to be ascertained. The Fixed cost is time-related, i.e. it remains constant over a Unlike Variable Cost which is volume related, i.e. it changes with the change in volume.
But he is not paying these amounts explicitly i.e. because he has contributed them for his own business. So market value of these self-owned and self-supplied inputs must be calculated. It is, therefore, a cost to the producer.
(d) When output is zero, total cost equals ____________ (fixed cost, variable cost).
What is Policy Cost – These are cost which are incurred by any business enterprise as a matter of policy. Research and development costs are generally https://1investing.in/ policy costs. It may be noted that controllable and uncontrollable cost concepts are related to the authority of a person in the organization.
These costs can be traced through invoices, receipts and quotations. What is Shut-down Cost – Shut-down costs are those which continue to be incurred even when a plant is temporarily shut-down. Depreciation, salaries of staff, etc. These costs cannot be eliminated with the closure of the plant. What is postponable Costs – These are the costs which can be shifted to a future period with little no effect on the efficiency of current operations.
It can be complicated because it involves many different kinds of circumstances. Therefore, it is difficult to provide a standard method for calculating implicit costs. In business accounts only explicit costs are treated as cost. He will either provide these inputs himself or he will purchase them from the market.
NIOS Economics Notes/Answer| Chapter-18| Cost. Important questions forNIOSEconomics Questions Answers brings you latest queries and solutions with accordance to the most recent pointersSOS. These queries can facilitate students prepare well for the exams thanks to time constraint . Supplies required by the company in order to supply its output to customers. Now keep track of your cashflow and manage your incomes and expenses with ease by using the Cashbookapp by Khatabook.
Implicit cost is an opportunity cost that arises from the allocation of resources. This cost is not reported separately but is not included in the accounting profit. In essence, it is the value of the opportunity created by using internal capital. The costs of direct materials, direct labor, etc. are example of variable cost.
It depicts a money transaction or the application of a tangible resource. An implicit cost is defined as a cost that has already been incurred but has not been explicitly expressed or reported as a separate expense. It reflects the value of an opportunity created when a company uses internal capital for a project with no clear reimbursement for resource usage.
(a) Average cost is ____________ (cost per unit, cost incurred on additional unit).
For example, the table given below shows TFC, TVC and TC. When we calculate MC from either TC or TVC we get the same result. Calculate yourself and the check the result. A firm purchases the services of assets like building machines etc.
Now, suppose, that the market for science books is more assured but profit is lower. This would mean that the publisher who is publishing commerce books is sacrificing an assured return on science books and is taking a risk. He would be prepared to face the risk only when he thinks that he would be able to get at least the same profit which he would have in any way got from science books. Loss of assured return on science books is then an element of cost for the publisher who is publishing commerce books instead of science books. It is termed as ‘normal profit’ because it is an estimate of the minimum expectations of a producer from a business. So long as he gets this minimum, he will continue to publish commerce books.
How to calculate the Explicit Cost?
What is Research Costs – There are costs incurred on the discovery of new or improved products, processes, methods of production, etc. How to say imputed cost in Hindi example of imputed cost and what is the meaning of imputed cost in Hindi? Imputed cost Hindi meaning, translation, pronunciation, synonyms and example sentences are provided by Hindlish.com.
It is nothing but the minimum assured profit in the next best occupation. Normal profit is the reward which an entrepreneur must receive for the risk and uncertainties he bears in the production of a commodity. It can be understood with an example. Suppose there is a publisher who has the option of publishing commerce books or science books. He chooses to publish commerce books because he gets higher return from these.
Imputed / Notional cost – CIMA defines notional cost as “the value of benefits where no actual cost is incurred”. Thus, imputed cost is that cost which does not involve any cash outlay. Though it is a hypothetical cost, it is relevant for decision making. Interest on capital, the payment for which is not actually made, is an example of imputed cost. Average Fixed Cost is per unit fixed cost in producing a commodity or fixed cost per unit of output. Average variable cost is per unit variable cost in producing a commodity or variable cost per unit of output.